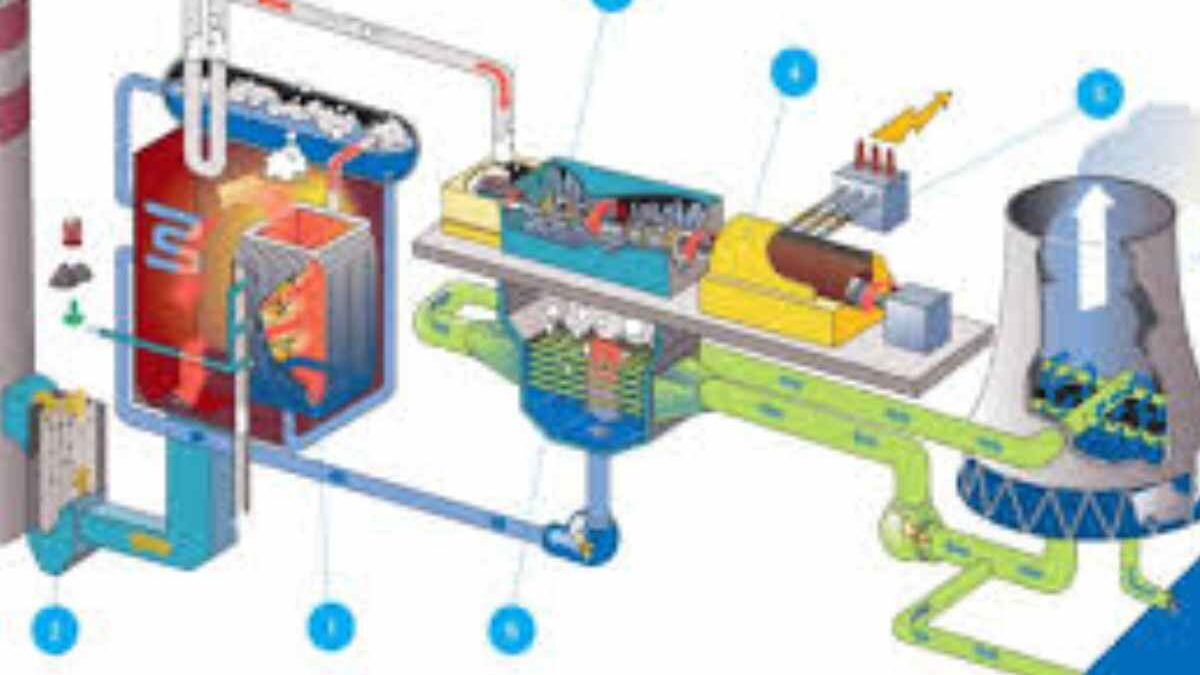
The Rankine cycle is a thermodynamics process involving a constant-pressure heat engine to convert heat into mechanical work. This heat is supplied externally in the cycle in a closed loop using different fluids such as toluene or plain water. William John Macquorn Rankine Was the Scottish engineer who developed a theory of the heat engine with the steam engine in 1859. This is why this ranking cycle was named after him in honor of his contribution to the subject.
The Rankine cycle is a theoretical cycle on which a power plant will work. It is the basic principle of steam turbines, also known as the modified Carnot cycle. This cycle will have a maximum efficiency.
Advantages of the Rankine Cycle
- The Rankine cycle will achieve high thermal efficiency, primarily in large-scale power plants. They will utilize a high-temperature scheme to get turbines and then convert a significant portion of the input heat into mechanical work.
- The circle is tremendous and is implemented using heat sources such as nuclear energy or fossil fuels. Other renewable sources, such as solar energy, are also used. This method will apply to a wide range of power generation systems.
- This cycle can be integrated into power systems and heat. Well, both are helpful heat and electricity are generated constantly. This simultaneous generation capacity will increase the overall effectiveness and usefulness of the system.
- The Rankine cycle will allow for condensation to happen at relatively low pressure. This process will reduce the stress on materials used in the condenser, eventually making the design and construction of condenser components easier.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are significant advantages of the Rankine cycle, but there are some limitations to it. Also, it would be best to remember that ongoing research and development aim to address issues and challenges to improve the cycle’s overall effectiveness and usefulness, especially when discussing environmental concerns and the push for more sustainable energy solutions.